More Coverage
Twitter Coverage
Satyaagrah
Written on
Satyaagrah
Written on
Satyaagrah
Written on
Satyaagrah
Written on
Satyaagrah
Written on
JOIN SATYAAGRAH SOCIAL MEDIA
"And the winds and the waves are always on the side of the ablest navigators": ISRO successfully launched GSLV-F12/NVS-01 Mission from SDSC-SHAR, Sriharikota, NVS-01 first of the India's second-generation NavIC satellites that accompany enhanced features
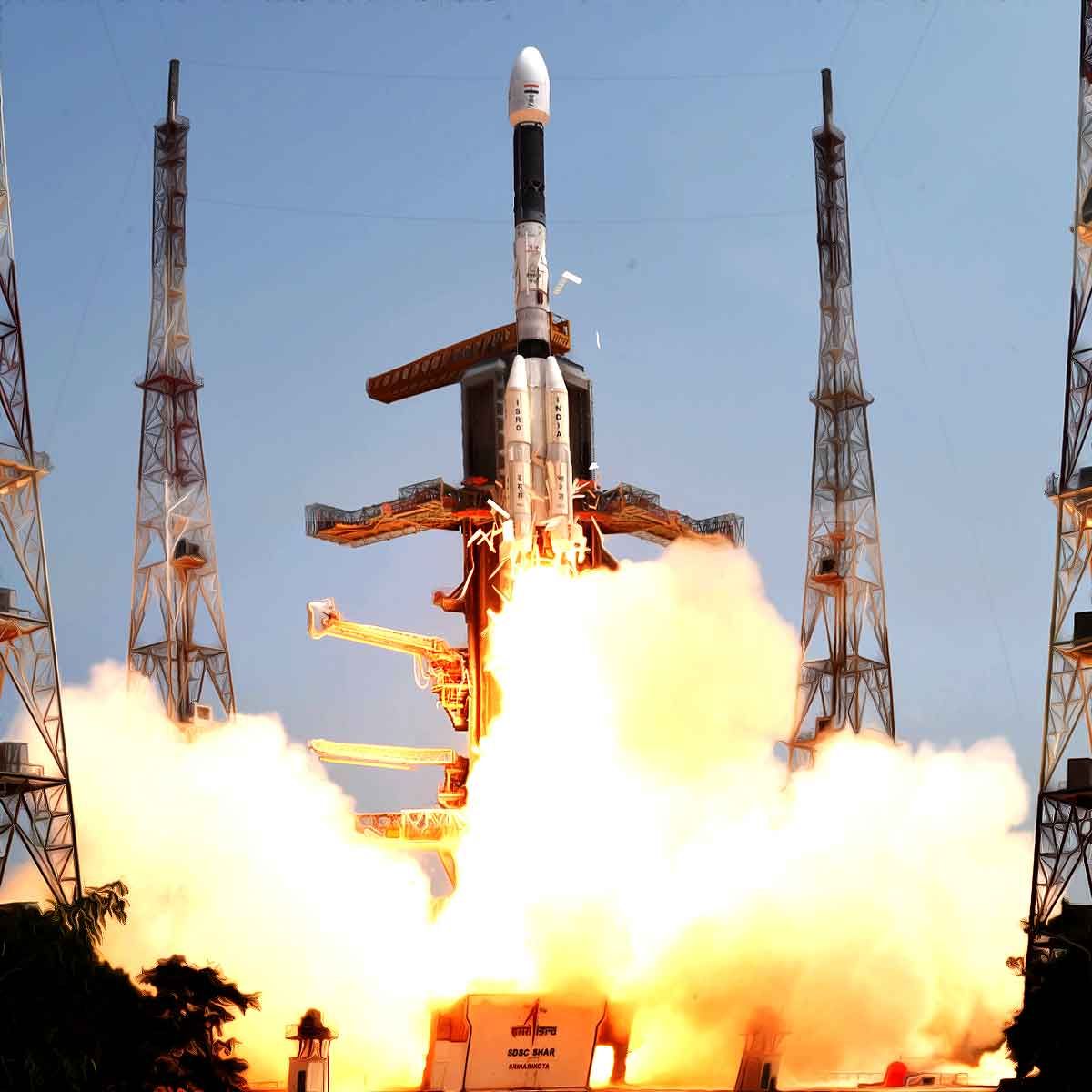

The launch of the GSLV-F12/NVS-01 mission is accomplished on Monday, May 29, 2023 at 10:42 hours IST from the second launch pad at SDSC-SHAR, Sriharikota. This Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) mission is designed to deploy the NVS-01 navigation satellite, weighing about 2232 kg, into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit. Subsequent orbit raising maneuvers will be used for taking the satellite to the intended orbit.
NVS-01 is the first of the second-generation satellites envisaged for the Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) services. NVS series of satellites will sustain and augment the NavIC with enhanced features. This series incorporates L1 band signals additionally to widen the services. For the first time, an indigenous atomic clock will be flown in NVS-01.
Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS): NavIC
India's space agency, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), has embarked on an ambitious project to launch its very own version of the Global Positioning System (GPS). This initiative, known as the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), aims to provide precise positioning and timing services for users within the Indian subcontinent and its neighboring regions. Let's delve into the details of this remarkable endeavor.
The genesis of IRNSS can be traced back to the early 21st century when ISRO recognized the need for an indigenous navigation system to cater to the unique requirements of the Indian region. The existing GPS, while highly capable, primarily serves the global community and has limited coverage in remote areas and dense urban environments. Recognizing this limitation, ISRO set out to develop a dedicated navigation system that would offer enhanced reliability, accuracy, and availability for Indian users.
The IRNSS comprises a constellation of satellites in geostationary and geosynchronous orbits. These satellites form the backbone of the navigation system, transmitting precise positioning and timing signals to ground-based receivers. The constellation typically consists of seven satellites, strategically positioned to ensure continuous coverage over the Indian subcontinent and a radius extending up to 1,500 kilometers beyond its borders.
Each IRNSS satellite is equipped with a variety of advanced payloads and instruments that enable it to deliver its intended services. The navigation payload on board these satellites generates highly accurate signals, which are broadcast in multiple frequency bands. This diversity of signals enhances the system's robustness, making it resilient against signal interference and improving the quality of navigation services even in challenging environments.
IRNSS satellites also carry atomic clocks that are incredibly accurate, ensuring precise timing synchronization across the entire system. This accurate timing information is essential for various applications, including telecommunications, financial transactions, power grid management, and disaster management systems.
To receive and decode the signals from the IRNSS satellites, users need compatible receivers. ISRO has collaborated with numerous industries and manufacturers to develop a wide range of receivers that cater to different sectors and user requirements. These receivers are designed to be compact, lightweight, and power-efficient, enabling their integration into various devices such as smartphones, vehicles, aircraft, and maritime vessels.
The benefits of IRNSS are multifaceted and have far-reaching implications for different sectors. In the field of transportation, the system enables precise vehicle tracking, route planning, and navigation assistance, thereby improving the efficiency of logistics and transportation networks. It also enhances the safety of maritime navigation by providing accurate positional information to ships and vessels, reducing the risk of accidents, and facilitating efficient search and rescue operations.
IRNSS has significant implications for the defense and security sectors as well. The system enables the Indian Armed Forces to enhance their operational capabilities through reliable and accurate positioning information. It aids in precision targeting, artillery guidance, and troop navigation, bolstering the overall effectiveness of military operations.
Moreover, IRNSS has proven instrumental in disaster management and emergency response scenarios. During natural calamities, such as earthquakes, floods, or cyclones, the system provides real-time positioning information to rescue teams, enabling them to reach affected areas promptly and efficiently. The accurate timing signals from IRNSS are also crucial for synchronizing emergency communication networks and coordinating relief efforts.
The development and deployment of IRNSS signify a significant technological achievement for India's space program. It demonstrates the nation's prowess in satellite navigation systems and reinforces its position as a global player in the field of space technology. Additionally, the self-reliance achieved through IRNSS ensures that India is not dependent solely on foreign navigation systems, further strengthening its national security and sovereignty.
ISRO's launch of India's version of GPS, the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), is a remarkable feat that brings advanced navigation capabilities to the Indian subcontinent and its neighboring regions. The constellation of IRNSS satellites, equipped with cutting-edge technology, provides highly accurate positioning and timing services across various sectors, including transportation, defense, disaster management, and telecommunications. This indigenous navigation system highlights India's technological prowess and self-reliance in space technology, propelling the nation into the league of global space leaders.
Some applications of IRNSS are:
- Terrestrial, Aerial, and Marine Navigation
- Disaster Management
- Vehicle tracking and fleet management
- Integration with mobile phones
- Precise Timing
- Mapping and Geodetic data capture
- Terrestrial navigation aid for hikers and travellers
- Visual and voice navigation for drivers
NavIC, which stands for Navigation with Indian Constellation, is the operational name given to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). NavIC is a highly sophisticated and indigenous satellite navigation system designed to provide precise positioning, navigation, and timing services to users within the Indian subcontinent and its surrounding regions.
The NavIC system consists of a constellation of seven satellites in orbit, with three satellites placed in geostationary orbit and the remaining four satellites positioned in geosynchronous orbits inclined at an angle to the equator. This unique configuration ensures continuous coverage and enhances the accuracy and reliability of the navigation signals across the vast Indian region.
|
Each NavIC satellite carries multiple payloads and instruments that contribute to the overall functionality of the system. The primary payload is the Navigation Payload, which generates highly accurate and reliable navigation signals. These signals are transmitted in multiple frequency bands, including L5 and S-band, to provide enhanced accuracy and improved resistance to signal interference caused by various environmental factors.
NavIC satellites also incorporate Rubidium Atomic Clocks, which are highly precise timekeeping devices. These atomic clocks ensure accurate synchronization of timing signals across the entire NavIC constellation, enabling users to have precise timing information for a wide range of applications.
To receive and process the NavIC signals, users require NavIC-compatible receivers. ISRO has collaborated with various manufacturers to develop a diverse range of receivers tailored to different user needs. These receivers can be integrated into various devices such as smartphones, tablets, navigation systems, vehicles, aircraft, and maritime vessels.
The benefits of NavIC extend across multiple sectors. In the field of transportation, NavIC enables precise vehicle tracking, navigation assistance, and efficient route planning, leading to improved logistics and enhanced road safety. The system also supports the aviation industry by providing accurate positioning and timing information to aircraft, enabling safer and more efficient air travel.
NavIC plays a crucial role in maritime navigation as well. It provides accurate positional information to ships and vessels, facilitating safe navigation through busy shipping lanes and reducing the risk of accidents. Additionally, NavIC aids in efficient search and rescue operations during emergencies at sea.
The defense and security sectors also benefit significantly from NavIC. The system enhances the capabilities of the Indian Armed Forces by providing precise positioning, navigation, and timing services, which are crucial for military operations, precision targeting, artillery guidance, and troop navigation.
Moreover, NavIC has proven instrumental in disaster management and emergency response scenarios. The system provides real-time positioning information to rescue teams during natural calamities, enabling them to reach affected areas promptly. The accurate timing signals from NavIC are also vital for synchronizing communication networks and coordinating relief efforts during emergencies.
|
NavIC represents a significant achievement for ISRO and India's space program. It showcases India's expertise in satellite navigation technology and highlights the nation's self-reliance in this critical domain. By developing and deploying NavIC, India has reduced its dependency on foreign navigation systems and strengthened its national security and sovereignty.
NavIC, the operational name for the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) developed by ISRO, is a state-of-the-art satellite navigation system designed to provide precise positioning, navigation, and timing services to users in the Indian subcontinent and its surrounding regions. With its advanced technology, diverse applications, and self-reliance, NavIC reinforces India's position as a global leader in space technology and contributes to the nation's overall development and security.
References:
 Support Us
Support Us
Satyagraha was born from the heart of our land, with an undying aim to unveil the true essence of Bharat. It seeks to illuminate the hidden tales of our valiant freedom fighters and the rich chronicles that haven't yet sung their complete melody in the mainstream.
While platforms like NDTV and 'The Wire' effortlessly garner funds under the banner of safeguarding democracy, we at Satyagraha walk a different path. Our strength and resonance come from you. In this journey to weave a stronger Bharat, every little contribution amplifies our voice. Let's come together, contribute as you can, and champion the true spirit of our nation.
 |  |  |
| ICICI Bank of Satyaagrah | Razorpay Bank of Satyaagrah | PayPal Bank of Satyaagrah - For International Payments |
If all above doesn't work, then try the LINK below:
Please share the article on other platforms
DISCLAIMER: The author is solely responsible for the views expressed in this article. The author carries the responsibility for citing and/or licensing of images utilized within the text. The website also frequently uses non-commercial images for representational purposes only in line with the article. We are not responsible for the authenticity of such images. If some images have a copyright issue, we request the person/entity to contact us at satyaagrahindia@gmail.com and we will take the necessary actions to resolve the issue.
Related Articles
- ISRO successfully tested the Gaganyaan Service Module Propulsion System (SMPS) on July 19, 2023 at ISRO Propulsion Complex (IPRC) , Mahendragiri
- The legend and a genius that was Jagadish Chandra Bose: Champion of East and West Who Almost Invented the Radio
- "There is no law except the law that there is no law": Samudrayaan with Matsya 6000 is set to unlock the ocean's enigmatic heart, heralding a new era in harnessing marine resources for a sustainable future symbolizing a big leap in deep-sea exploration
- "Historic launch of Chandrayaan-3": A lunar mission set to make India the fourth nation to land on the moon, encompassing technological marvel, scientific discovery, and national pride, carving out India's place in the annals of space exploration
- "Research is creating new knowledge, without which there is no progress": National Research Foundation - a visionary initiative by the Indian govt aimed at centralizing funding for scientific & academic research with an ambitious target of ₹50,000 crore
- "Beyond gravity, within safety": ISRO's Gaganyaan mission progresses with Drogue Parachute tests, prioritizing astronaut safety, aiming to send a crew to 400 km orbit for 3 days, it utilizes Human Rated LVM3 and comprehensive training in Bengaluru
- Chandra - NASA’s advanced X-Ray Observatory is named after a brilliant Indian scientist & Nobel Prize-winner Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar, a Flagship-class space telescope is an Earth satellite in a 64-hour orbit, notably its mission is ongoing as of 2023
- "India's cosmic journey: From moonbeams to sunrays": ISRO's landmark Aditya-L1 mission set to launch, promising 24x7 Sun surveillance, aiming to decode solar mysteries, it will enhance our understanding of space weather and the profound Sun-Earth dynamics
- Are We Alone in the Universe? NASA hints at the possibility of extra-terrestrial life, wants to establish New framework
- "We live in a world defined by the rapid pace of technological change": India is experiencing tremendous economic growth under PM Modi. Look forward to continuing our strong partnership and supporting India's G20 presidency - Google CEO Sundar Pichai
- Ten most compelling evidence of Extraterrestrial existence from 2020
- In a world where robots fetch more, even the canniest of canines find themselves in a tail-wagging contest of wits & whimsy; Muks Robotics rolls out the red carpet for AI, sparking a playful rivalry that leaves every dog wondering who's really the top dog
- "Innovation is the calling card of the future": Jaldost, a revolutionary airboat by Bengaluru's National Aerospace Laboratories, powers through aquatic weeds, carving the path towards preserving cleaner water bodies, a testament to indigenous innovation
- “Genius is never understood in its own time”: Do you know when you put your debit card in ATM and ask for money, machine arranges the money before giving it to you using Srinivasa Ramanujan’s partition theory, celebrated as National Mathematics Day
- "Ambition is path to success. Persistence is the vehicle you arrive in": India scripted history as ISRO successfully launches 36 OneWeb broadband satellites in heaviest LVM3-M2 rocket on its debut commercial mission, all satellites separated successfully